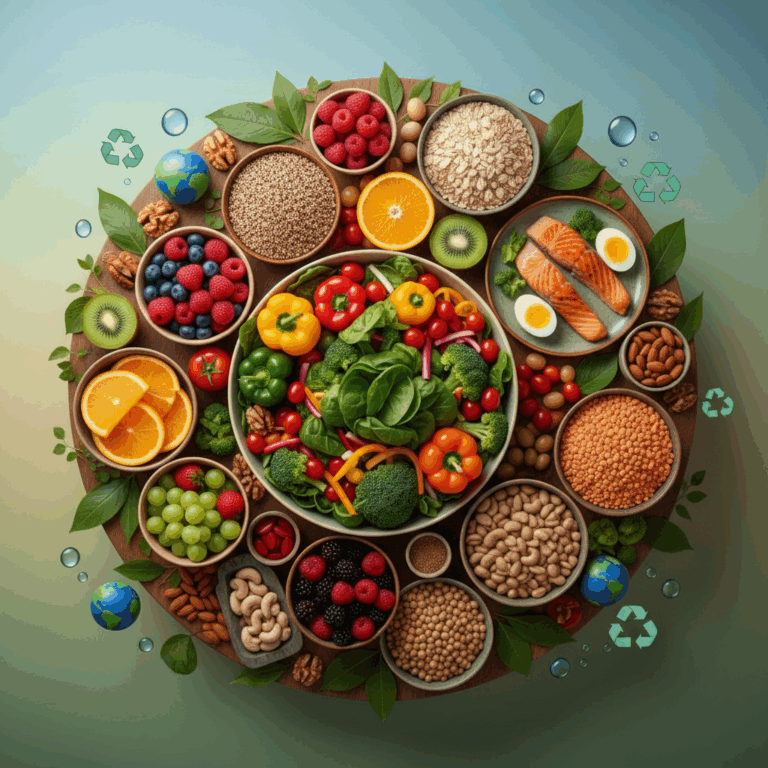Announcements
Concept and objectives of the planetary diet
The planetary diet it is a food model based on scientific principles that seeks to promote healthy and, at the same time, sustainable eating.
Its origin arises in response to the environmental crisis and health problems linked to traditional food, promoting urgent changes in habits.
Announcements
This diet aims to balance human well-being and environmental protection to generate a positive impact on the planet and its inhabitants.
Definition and scientific origin
The planetary diet, or “climatarian”, was developed by the EAT-Lancet Commission to establish dietary guidelines that reduce environmental damage.
Announcements
Its scientific basis analyzes the ecological footprint of different foods, promoting greater consumption of plants and lower intake of products with a high footprint.
This approach helps mitigate greenhouse gas emissions from food production, accelerating the fight against climate change.
It is a model that integrates public health and environmental sustainability to achieve more responsible and balanced food systems.
Environmental and health objectives
The planetary diet seeks to reduce global emissions caused by food, which represent around a third of polluting gases.
Encourage the consumption of local, seasonal, organic foods low in red meat and dairy to reduce the environmental footprint.
In health, it has been shown that this diet reduces the risks of cardiovascular diseases, cancer and premature mortality by up to 30%.
Its mass adoption could prevent millions of deaths a year and reduce the incidence of chronic diseases, promoting a healthier future for all.
Dietary principles of the planetary diet
The planetary diet emphasizes the consumption of foods that have a lower environmental impact, prioritizing sustainable plants and products.
Promotes a balanced diet that protects both human health and the planet's natural resources.
These principles guide food selection to achieve a fair and ecologically viable food system.
Recommended foods and their origin
It is recommended to increase the intake of fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts and whole grains, preferably organically produced.
Local and seasonal provenance is key to reducing carbon footprint and supporting sustainable agricultural systems.
Moderate consumption of sustainable fish is also part of this guide, promoting healthy marine ecosystems.
These choices contribute to biodiversity and improve the nutritional quality of the diet.
Foods to reduce or avoid
It is suggested to drastically limit red meat and dairy products, which generate a high environmental footprint and impact on health.
In addition, it is recommended to avoid ultra-processed foods and added sugars, which harm health and the environment.
Reducing these foods helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions and prevents chronic health problems.
This approach promotes a more natural and environmentally conscious diet.
Importance of local and seasonal production
Consuming local and seasonal products reduces emissions linked to refrigerated transportation and storage.
This practice strengthens the local economy and reduces waste, contributing to global food sustainability.
Production aligned with natural cycles respects ecosystems and guarantees fresher and more nutritious food.
Interesting fact
Food waste is responsible for 10% of global greenhouse gas emissions, its reduction being crucial.
Environmental impact of the current food system
The global food system contributes significantly to climate change, being responsible for a third of global greenhouse gas emissions.
These emissions come mainly from animal production, the use of fertilizers and intensive agricultural practices, compromising planetary health.
Transforming the food system is essential to reduce environmental impact and ensure a sustainable future.
Greenhouse gas emissions
Current food production and consumption generate approximately 30% of greenhouse gases worldwide.
Red meat and dairy products have a particularly high environmental footprint due to methane release and resource-intensive use.
Adopting a plant-based diet significantly reduces these emissions, favoring the mitigation of climate change.
Thus, the planetary diet seeks to reduce dependence on foods with a high footprint to protect climate balance.
Reduction of waste and transportation
Food waste contributes about 10% of global emissions, making it a considerable source of avoidable pollution.
Unconsumed food ends up in landfills where it generates polluting gases, so reducing waste is vital for sustainability.
On the other hand, prioritizing local and seasonal products reduces emissions related to transportation and refrigeration.
These combined actions strengthen the local economy and minimize the ecological footprint of the food system.
Health and sustainability benefits
The planetary diet offers comprehensive benefits, improving individual health and promoting environmental sustainability by adopting responsible eating habits.
By choosing plant-based foods and sustainable practices, you create a virtuous cycle that protects both people and the planet.
This approach represents an opportunity to reduce the burden of disease while simultaneously reducing global environmental impact.
Reduction of risks of diseases and mortality
Following the planetary diet reduces the risk of premature death related to chronic diseases such as cardiovascular diseases and cancer by up to 30%.
Including fruits, vegetables, legumes and whole grains strengthens the immune system and helps prevent important health diagnoses.
In addition, this diet helps control growing problems such as diabetes and obesity, promoting a higher quality of life.
Contribution to environmental protection
Adopting the planetary diet helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions generated by the food industry, key in the fight against climate change.
The preference for local, seasonal foods with a smaller ecological footprint protects biodiversity, soils and water quality.
By reducing food waste and the consumption of products with a high environmental footprint, this diet promotes fairer and more sustainable food systems.