Announcements
Relationship between diet and emotional state
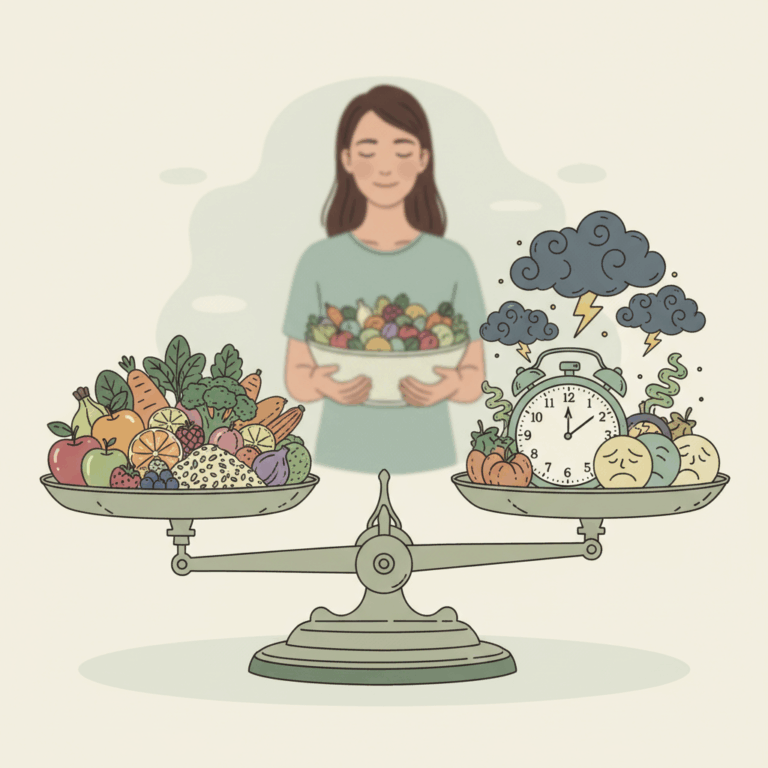
The diet it plays a crucial role in the emotional balance, since it directly influences brain chemistry. Specific nutrients can significantly improve mood.
A balanced diet, rich in fresh and natural foods, is essential for the proper functioning of the nervous system and for the proper management of stress and anxiety.
Announcements
Including fruits, vegetables, whole grains and healthy fats helps maintain stable emotional well-being and prevent psychological imbalances.
Nutrients that affect brain chemistry
Several nutrients act directly on brain chemistry, influencing the production of key neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine. These regulate mood and stress response.
Announcements
Tryptophan, present in foods such as turkey, eggs and cheese, is essential for the synthesis of serotonin, the neurotransmitter of happiness and emotional well-being.
B complex vitamins, minerals and omega-3 fatty acids provide the necessary support to maintain brain health and promote positive and stable emotional states.
Role of neurotransmitters in mood and stress
Neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine regulate emotions, stress and anxiety, acting as messengers that control communication between neurons.
An adequate nutritional contribution facilitates its production and balance, resulting in better emotional control and reduction of symptoms related to stress.
Therefore, one balanced diet it is key to maintaining optimal levels of these compounds and promoting a healthy emotional state.
Foods that promote emotional balance
Consume fresh and natural foods it is essential to maintain optimal emotional balance. These provide vital nutrients that positively impact brain chemistry and well-being.
Including fruits, vegetables, whole grains and legumes in the daily diet can improve the production of neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine, mood and stress regulators.
In addition, a healthy diet helps control anxiety and promotes a stable emotional state, essential to face daily demands with greater resilience.
Recommended fresh and natural foods
It is important to prioritize fresh foods such as fruits and vegetables, which contain antioxidants, vitamins and minerals essential for brain and emotional health.
Whole grains provide constant energy and fiber, helping to maintain a stable blood glucose level, essential for brain function and mood.
Legumes and nuts are sources of proteins and healthy fats that promote the production of neurotransmitters and strengthen the nervous system.
Specific nutrients with positive effect
Tryptophan, present in foods such as turkey, eggs and cheese, is key to the synthesis of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that regulates happiness and emotional well-being.
B complex vitamins act as cofactors in brain metabolic reactions, improving cognitive functions and modulating stress.
Likewise, minerals such as magnesium and zinc contribute to reducing anxiety and stabilize the nervous system, promoting better emotional management.
Importance of healthy fats such as omega-3
Omega-3 fats, present in fatty fish, seeds and nuts, are essential for the structure and function of neurons that regulate emotions.
These fatty acids improve neuronal communication and have anti-inflammatory properties that protect the brain, contributing to better emotional balance.
Including sources of omega-3 in your daily diet is essential to prevent mood disorders related to stress and anxiety.
Impact of stress on eating habits
Stress can significantly alter eating habits, creating confusion between emotional hunger and real hunger. This distinction is essential to maintaining a healthy diet.
Understanding how stress influences the way we eat allows us to adopt strategies to avoid bad habits that can harm emotional balance and increase anxiety.
Conscious eating provides benefits by controlling consumption impulses, especially when it comes to ultra-processed foods, which are usually preferred in times of stress.
Distinction between emotional hunger and real hunger
Emotional hunger arises in response to negative feelings, seeking comfort in food, while real hunger is physical and gradual, motivated by the body's energy needs.
Recognizing these differences is key to avoiding excessive consumption of foods rich in sugars and fats, which can generate a negative cycle in emotional and physical regulation.
Emotional hunger usually appears suddenly and with specific cravings, contrasting with real hunger, which is progressive and can be satisfied with a variety of nutritious foods.
Conscious diet to avoid ultra-processed foods
Conscious diet invites you to pay full attention to the body's signals, promoting food choices that promote mental health and avoid the consumption of ultra-processed foods rich in harmful additives.
Avoiding these foods helps control sugar spikes and mood disturbances that enhance stress, improving emotional balance and daily energy.
Implementing habits such as planning meals, choosing natural ingredients and respecting eating times strengthens resistance to stress and promotes better general well-being.
Intestinal microbiota and emotional modulation
The intestinal microbiota it plays a critical role in brain function through the production and regulation of neurotransmitters. Its balance is key to emotional stability.
An adequate diet directly influences the composition of this microbiota, favoring the production of substances that affect mood and stress management.
Therefore, the relationship between intestinal health and emotional modulation is a growing field, highlighting the importance of taking care of your diet to improve mental well-being.
Relationship between microbiota and neurotransmitter production
The intestinal microbiota generates compounds that enhance the synthesis of neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine, essential for regulating emotions and reducing anxiety.
In addition, certain microorganisms promote the production of short-chain fatty acids that influence communication between intestine and brain, improving emotional health.
An imbalance in the microbiota can worsen symptoms of stress and mood disturbances, so maintaining its integrity is essential for psychological balance.
Benefits of taking care of your diet for mental health
A diet rich in fiber, probiotics and prebiotics helps maintain a healthy microbiota, which in turn improves the production of neurotransmitters related to happiness.
This reduces brain inflammation and promotes better control of stress and anxiety, increasing emotional resilience and quality of life.
Eating fermented foods, fruits, vegetables and whole grains is an effective strategy to enhance mental health through intestinal care.