Announcements
Intestinal microbiota and its importance for health
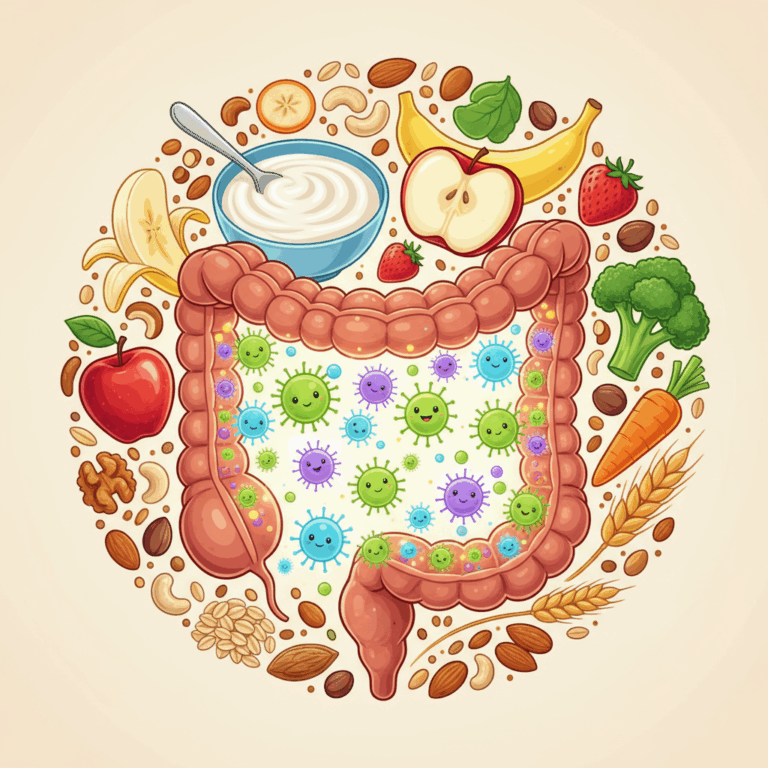
The intestinal microbiota it is made up of millions of microorganisms that live in our intestine, playing a vital role in digestive and metabolic functions.
Its balance directly influences the general health, affecting everything from the immune system to the absorption of essential nutrients for the body.
Announcements
Understanding its function and how to keep it healthy is key to preventing various diseases and improving daily well-being.
Definition and function of the intestinal microbiota
The intestinal microbiota is a set of bacteria, viruses and fungi that colonize the intestine and help process food and synthesize vitamins.
Announcements
Its main function is to maintain the balance of the digestive system, support digestion and protect against harmful pathogens.
In addition, it contributes to the development of the immune system and regulates inflammatory processes in the body.
Impact of the microbiota on general health
A balanced microbiota improves digestion, strengthens the immune system and reduces risks of metabolic and autoimmune diseases.
It also influences mental health, as it produces neurotransmitters that affect mood and brain function.
Alterations in this flora can cause problems such as inflammation, obesity, allergies and frequent digestive disorders.
Foods that strengthen the digestive flora
To maintain one healthy intestinal flora, it is essential to consume foods that promote the growth of beneficial bacteria. These foods include fiber, probiotics, and prebiotics.
Incorporating these nutrients into the daily diet improves digestion, strengthens the immune system and promotes general intestinal balance.
Knowing which foods provide these benefits helps you make informed decisions to take care of your intestinal health in the long term.
Foods rich in fiber and their effect
Foods rich in fibers they stimulate the growth and activity of healthy bacteria in the intestine, promoting digestion and intestinal transit.
Examples include fruits such as kiwi, blackberries and raspberries, as well as legumes such as lentils and chickpeas, which provide soluble and insoluble fiber.
Dried fruits such as raisins and dates also provide fiber that helps maintain a balanced digestive flora and reduce slow transit.
Probiotics: characteristics and sources
The probiotics they are live bacteria that, when consumed in adequate quantities, strengthen the microbiota and improve intestinal health.
They are found in fermented foods such as natural yogurt, kefir, kombucha and sauerkraut, which provide beneficial active microorganisms.
These foods not only improve digestion but also boost the immune system and help prevent infections.
Prebiotics: definition and key foods
The prebiotics they are indigestible fibers that serve as food for beneficial bacteria, stimulating their growth in the intestine.
They are found in foods such as onion, garlic, artichoke, banana and whole grains such as oats, which promote the proliferation of bifidobacteria and lactobacilli.
Regular consumption of prebiotics helps maintain a balanced and functional intestinal ecosystem, essential for general health.
Benefits of fermented foods for the intestine
The fermented foods they are a natural source of probiotics that improve the composition of the intestinal microbiota and its functioning.
Including these foods in the diet contributes to better digestion, nutrient absorption and a more balanced digestive system.
In addition, they promote the production of beneficial compounds that strengthen the intestinal barrier and reduce inflammation.
Examples and properties of fermented foods
Fermented foods include natural yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi and kombucha, rich in active probiotic bacteria.
These foods provide digestive enzymes and bioactive substances that improve intestinal health and contribute to microbial balance.
Its regular consumption favors the reduction of pathogens and promotes an ideal environment for the development of beneficial bacteria.
Thanks to fermentation, these products also have greater nutrient bioavailability and greater nutritional value.
Influence on the immune system
Probiotics present in fermented foods modulate the immune response, helping to strengthen the body's defenses.
They improve the production of antibodies and activate immune cells that protect against infections and diseases.
In addition, they contribute to the regulation of inflammatory processes, reducing the risk of autoimmune diseases and allergies.
Habits to preserve a healthy microbiota
Keep one healthy microbiota requires more than a balanced diet; It includes lifestyle habits that promote intestinal balance.
Proper hydration and physical activity are essential to promote an optimal environment where beneficial bacteria can develop and act.
Incorporating these habits into your daily routine helps improve digestive health and overall well-being, supporting the immune system.
Importance of hydration
The hydration adequate is essential to maintain the correct functioning of the intestine and facilitate intestinal transit.
Water helps dissolve nutrients and facilitates the elimination of toxins, creating an environment suitable for the proliferation of beneficial bacteria.
In addition, good hydration prevents constipation, a factor that can alter the balance of the microbiota and affect its health.
Therefore, it is recommended to drink between 1.5 and 2 liters of water per day, varying depending on physical activity and climate.
Role of physical activity in intestinal balance
The physical activity regular promotes intestinal motility, which contributes to better transit and a more diverse and balanced microbiota.
Moderate exercise reduces intestinal inflammation and promotes the production of compounds that benefit healthy bacteria.
It also improves blood circulation and the immune system, reinforcing the body's defense against pathogens and digestive disorders.